DataScience Blog
Python- Part 6
September 15, 2020
Check below commands. The next set…
Merge Dataframes
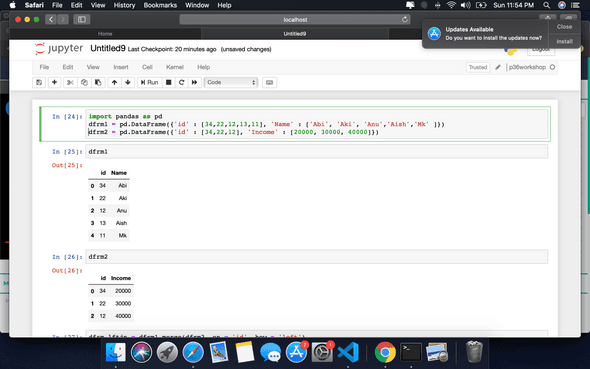
import pandas as pd
dfrm1 = pd.DataFrame({‘id’ : [34,22,12,13,11], ‘Name’ : [‘Abi’, ‘Aki’, ‘Anu’,‘Aish’,‘Mk’ ]})
dfrm2 = pd.DataFrame({‘id’ : [34,22,12], ‘Income’ : [20000, 30000, 40000]})
Output
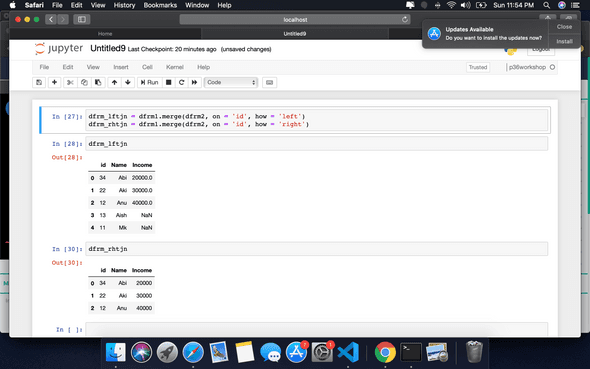
Joins
dfrmlftjn = dfrm1.merge(dfrm2, on = ‘id’, how = ‘left’)
dfrmrhtjn = dfrm1.merge(dfrm2, on = ‘id’, how = ‘right’)
Output
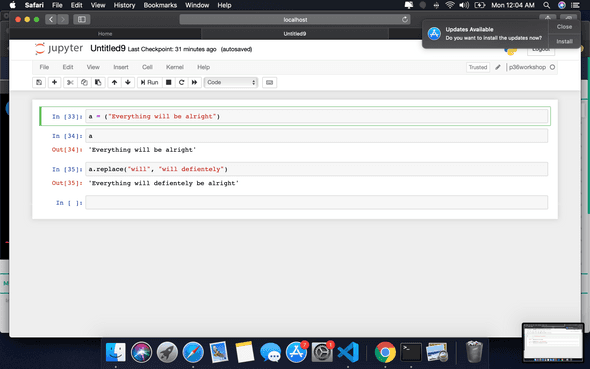
Replace values in a variable
a = (“Everything will be alright”)
a.replace(“will”, “will defientely”)
Output
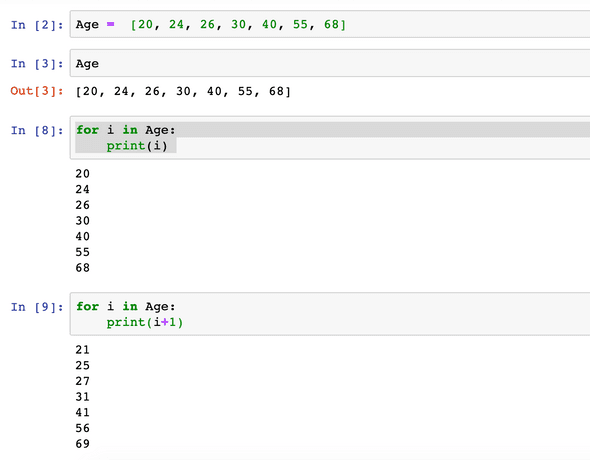
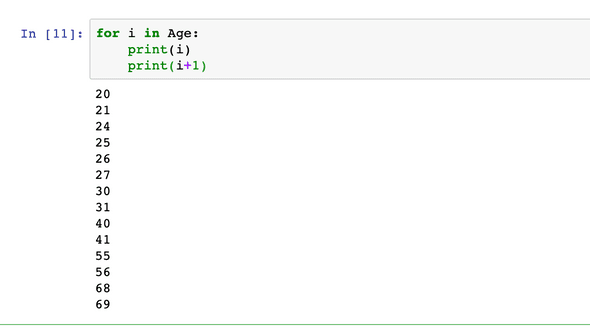
Create Vector & Sample Loop
Age = [20, 24, 26, 30, 40, 55, 68]
for i in Age
print(i)
print(i+1)
Make sure print statement starts after a single space. Else Indentation error will occur.
I have shown the output by running few commands..Check it
Output
Loading csv and checking length
import os
import pandas
os.chdir(“/Users/mac/Desktop/new/Python”)
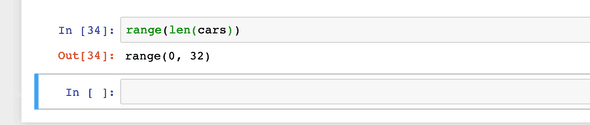
cars = pd.read_csv(“mtcars.csv”)
range(len(cars)) // checking the length
Output
We have 0 to 32 rows in the cars object.
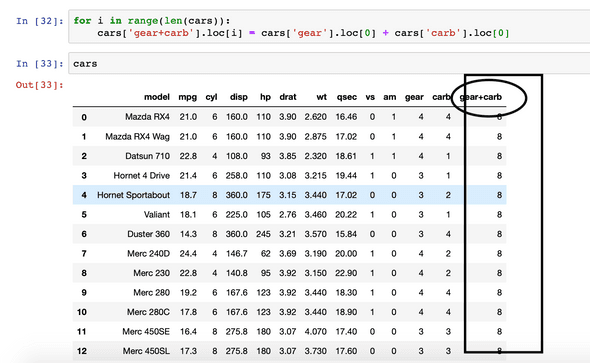
Adding new column using loop
We have columns named gear and carb in cars. Lets create a new variable named gear+carb which will be the sum of carb for every row.
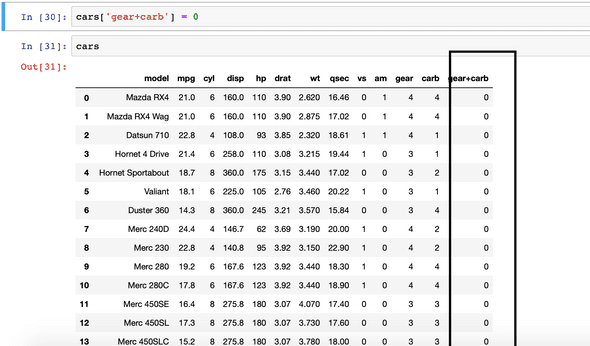
cars[‘gear+carb’] = 0 //new column created initially as 0
cars //checking the new column
for i in range(len(cars)):
cars[‘gear+carb’].loc[i] = cars[‘gear’].loc[0] + cars[‘carb’].loc[0]
cars //checking finally
Output
With this will end up python.. Lets execute the commands while we work on some projects and see how useful all these. Stay tuned for more important parts of Datascience which will be covered in upcoming posts.